一、go语言的并行执行
go语言的一大优势就是并行(go routine)执行,使用方便快捷、简洁。
下面是一个并行执行的代码示例,新建了一个函数run_cmd,用os/exec来执行外部拼接好的字符串。同时通过sync.WaitGroup来管理当前启动的程序,新程序启动时wg加一,某程序执行完wg减一。在主程序中用wg.wait()等待所有程序执行完再退出。
package main
import (
"os"
"os/exec"
"sync"
"fmt"
)
var wg sync.WaitGroup
func run_cmd (cmd_string string, id int) {
defer wg.Done()
fmt.Printf("cmd(%d) start...\n", id)
cmd := exec.Command("sh", "-c", cmd_string)
cmd.Stdin = os.Stdin
cmd.Stdout = os.Stdout
cmd.Stderr = os.Stderr
cmd.Start()
cmd.Wait()
fmt.Printf("cmd(%d) done\n", id)
}
func main() {
# start first cmd
wg.Add(1)
go run_cmd(cmd_string, 1)
# start second cmd
wg.Add(1)
go run_cmd(cmd_string, 2)
# wait all cmd done
wg.Wait()
fmt.Println("exit")
}
二、并行ict转captable
我们有三个ict文件,文件名如下,只有corner名字不同。
> ls
QRC_018V3EBCD_1P3M_2Ia_1MTT2_1stMIM20_CMAX.ict
QRC_018V3EBCD_1P3M_2Ia_1MTT2_1stMIM20_CMIN.ict
QRC_018V3EBCD_1P3M_2Ia_1MTT2_1stMIM20_TYPICAL.ict
新建一个corners的字符串数组,用for range来对每个corner进行迭代。拼接好字符串之后,直接调用go run_cmd即可。
func main() {
corners := []string{"CMAX", "CMIN", "TYPICAL"}
for i, c := range corners {
wg.Add(1)
cmd_string := "generateCapTbl -lef ../../SCC018V3EBCD_TF_V0p7/innovus/scc018v3ebcd_1p3m_2ia_1mtt2.lef -ict QRC_018V3EBCD_1P3M_2Ia_1MTT2_1stMIM20_" + c + ".ict -output QRC_018V3EBCD_1P3M_2Ia_1MTT2_1stMIM20_" + c + ".captable"
go run_cmd(cmd_string, i)
}
wg.Wait()
fmt.Println("exit")
}
三、运行go脚本
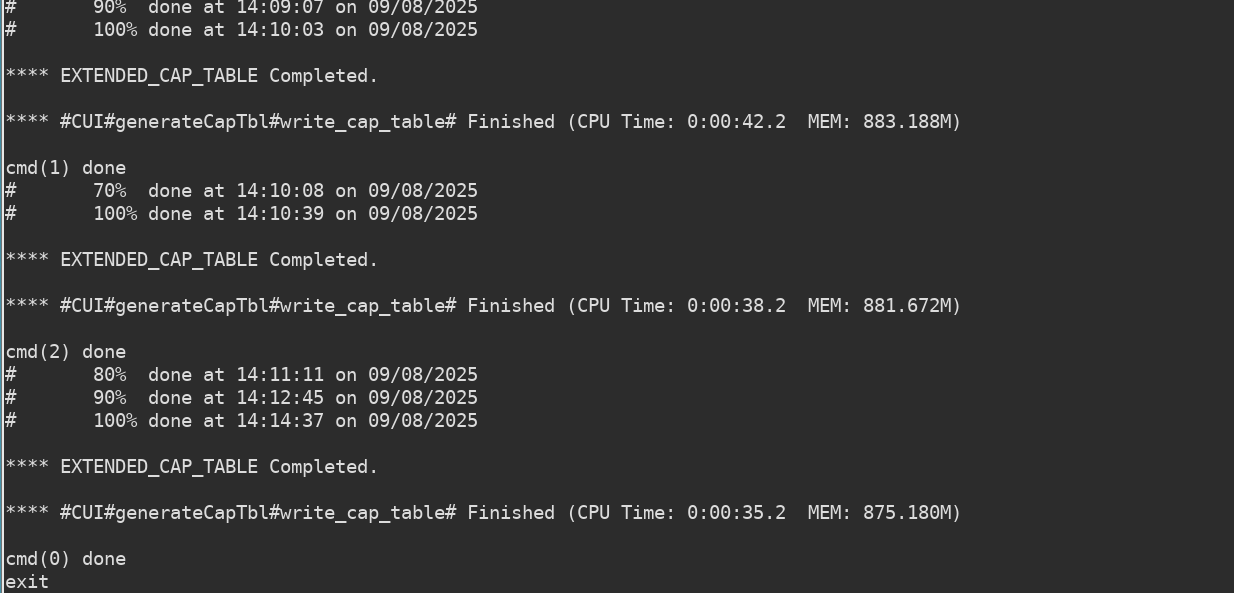
运行后,启动log如下,可见三个corner在并行跑。也可以用top来看到效果。
[test@host ICT] $ go run ict2captable.go
cmd(2) start...
cmd(0) start...
cmd(1) start...